Athlete’s Foot

What is Athlete’s Foot?
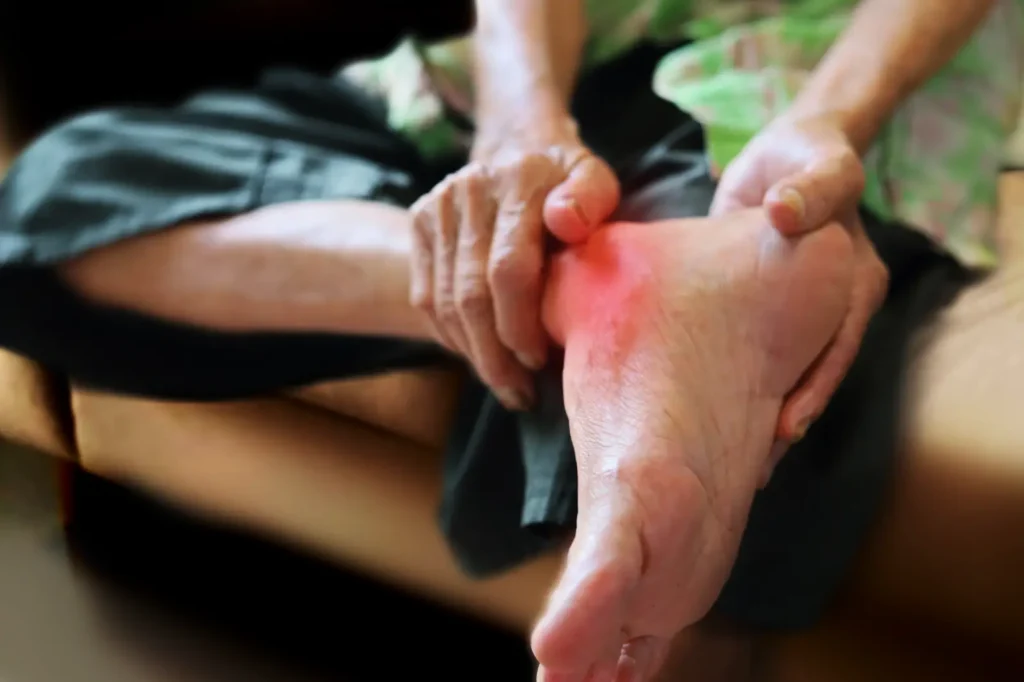
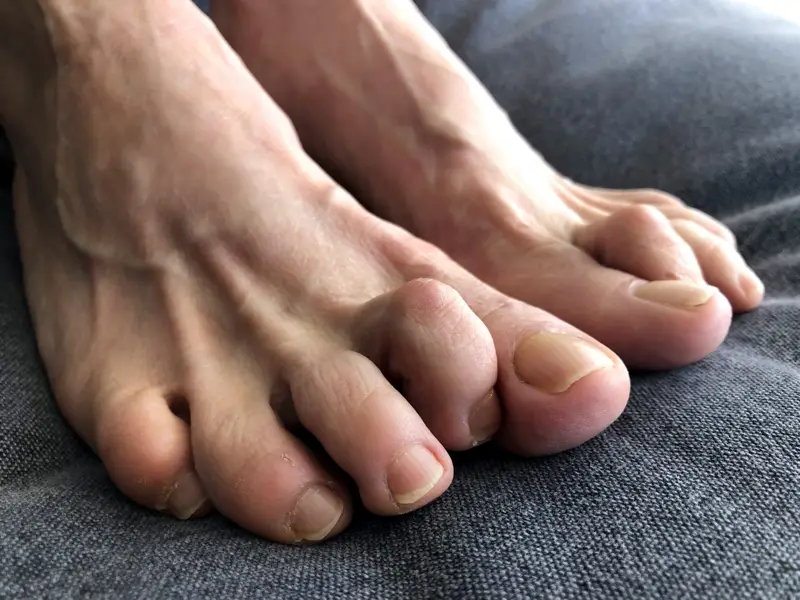
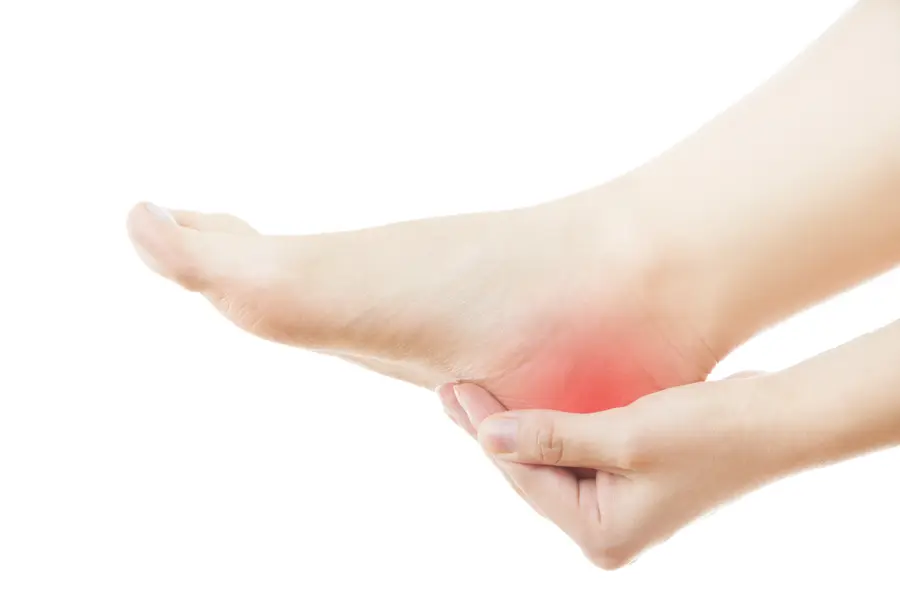
Athlete’s foot, medically known as tinea pedis, is a fungal infection that affects the skin on the feet. It’s part of a group of fungal infections called tinea. Athlete’s foot most commonly occurs between the toes but can affect the soles and sides of the feet.
What are the signs and symptoms of Athlete’s Foot?
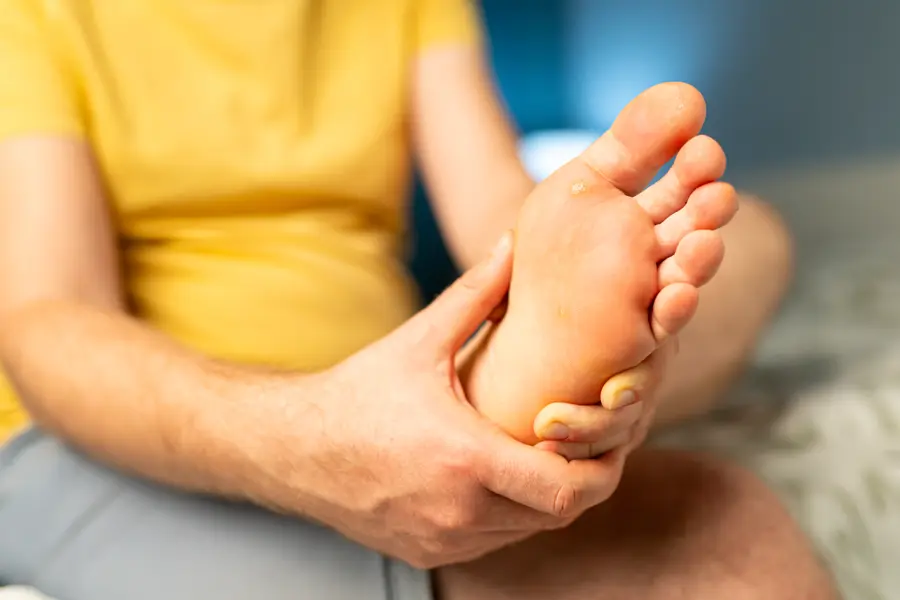
- Itching, stinging, and burning sensations between the toes or on the soles of the feet
- Cracked, flaky, or peeling skin in the infected area
- Redness and scaling on the feet
- Blisters or ulcers that itch or are painful
- Dry skin on the soles or sides of the feet

Athlete’s Foot FAQ
For a proper diagnosis and recommended treatment plan, we suggest you consult with a podiatrist for professional help and care.